Collaborate
Subscription confirmed
 WELCOME TO FLEET NEWS with regular updates from the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies.
WELCOME TO FLEET NEWS with regular updates from the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies.
Each edition of FLEET News brings a selection of research news from around the Centre, a wrap-up of FLEET stories in the media, outreach, and other news regarding FLEET researchers and research.
Catch up on past issues of FLEET News.
Michael Fuhrer
Director, FLEET
ARC Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies
Following the news
 If you’re on Facebook, Twitter or Linkedin, you can follow our accounts to stay up to date with FLEET news and events. You can also follow news and events at FLEET.org.au.
If you’re on Facebook, Twitter or Linkedin, you can follow our accounts to stay up to date with FLEET news and events. You can also follow news and events at FLEET.org.au.
If a friend or colleague might be interested in our news, send them this link. Or let us know and we’ll invite them.
The challenge
 The big challenge that FLEET is addressing is the increasing energy load of computation, which is currently at least 5% of world electricity use, and doubling each decade.
The big challenge that FLEET is addressing is the increasing energy load of computation, which is currently at least 5% of world electricity use, and doubling each decade.
To date, the amount of energy being burned by computing has been kept in check by a phenomenon known as Moore’s Law, whereby the number of chips in a given area doubles every two years. But we are fast approaching a limit for Moore’s Law.
Current computing is based on semiconductor chips that each burn a tiny, tiny amount of power as they ‘switch’. FLEET will develop switches that will burn almost zero energy, operating at room temperature.
Our research
FLEET will use new concepts for electronic conduction without resistance to create a new generation of ultra-low energy electronics.
We will develop materials in which electricity can flow with minimal resistance and dissipation of heat, and devices in which that electric current can be switched on and off.
FLEET’s three Research Themes are:
- Topological materials (led by Alex Hamilton, UNSW)
- Exciton superfluids (Elena Ostrovskaya, ANU)
- Light-transformed materials (Kris Helmerson, Monash)
And this research is underpinned by two Technology themes:
- Fabrication of atomically thin materials (Xiaolin Wang, University of Wollongong)
- Nanodevice fabrication (Lan Wang, RMIT)
About FLEET

With over $40M investment from the ARC (Australian Research Council) and contributing organisations, FLEET will make a significant global impact in the electronics and energy sectors.
Headquartered at Monash University, and an ARC Centre of Excellence, FLEET has 19 chief investigators at seven Australian institutions, 17 partner investigators at 13 institutions worldwide, and will have over 100 higher-degree research students and postdoctoral fellows.
The highly interdisciplinary team includes some of Australia’s best researchers in atomic physics, condensed matter physics, materials science, electronics, nanofabrication and atomically thin materials.
By building strategic and strong partnerships with Australian and international industry, research institutions and government, FLEET will build capacity for advanced electronics research in Australia and train the workforce for the next generation of electronic materials researchers and future semiconductor industry.
Recent news
Encasing fragile 2D materials in ultrathin gallium-oxide glass could allow integration into functional low-energy devices Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors have emerged during the past decade as extremely promising for future electronic and optoelectronic devices. However, to unlock the significant potential of these fragile materials, we must first find a way to protect them in functional devices, while maintaining their key electronic …
A new type of ultra-efficient, nano-thin material could advance self-powered electronics, wearable technologies and even deliver pacemakers powered by heart beats. The flexible and printable piezoelectric material, which can convert mechanical pressure into electrical energy, has been developed by an Australian research team led by RMIT. It is 100,000 times thinner than a human hair and 800% more efficient than …
“Stripy zebra, spotty leopard, …”. Kids never become bored pinpointing animals based on their unique body patterns. While it is fascinating that living creatures develop distinct patterns on their skin, what may be even more mysterious is their striking similarity to the skin of frozen liquid metals. Pattern formation is a classic example of one of nature’s wonders that scientists …
Important step towards fault-tolerant quantum computing Why is studying spin properties of one-dimensional quantum nanowires important? Quantum nanowires–which have length but no width or height–provide a unique environment for the formation and detection of a quasiparticle known as a Majorana zero mode. A new UNSW-led study overcomes previous difficulty detecting the Majorana zero mode, and produces a significant improvement in …
With strict Covid-19 restrictions across much of FLEET’s Australian nodes, and eliminating international visitors, the decision was made to hold the Centre’s 2020 annual workshop entirely online. By this time, Centre decision-makers were well aware of ‘Zoom fatigue’. People spending many hours on Zoom each week were finding interacting only via computer screen to be dis-engaging, and surprisingly exhausting. In …
Topological transistors added to IEEE International Roadmap for Devices and Systems The remarkable advances in semiconductor technology (guided by the so-called ‘Moore’s Law’ over some six or seven decades) don’t just happen. They are steered through an international, pre-competitive industry roadmap. The IEEE International Roadmap for Devices and Systems ‘IRDS’ is the latest semiconductor roadmap, guiding development of more conventional …
FLEET turbo-charged our existing Centre-wide seminar series in 2020, with 10 research seminars – a significant increase from only four seminars in 2019. Very aware of the importance of Centre cohesion without inter-state travel and with many universities in lockdown, FLEET threw extra resources into monthly Zoom seminars, often overlapping with expanded ‘journal club’ meetings involving multiple interstate visitors. Two …
In January 2020 FLEET brought the 10th International Conference on Spontaneous Coherence in Excitonic Systems (ICSCE10) to Australia for the first time. Continuing this 15-year tradition from the global scientific community interested in various quantum phenomena, ICSCE10 was hosted at the Arts Centre Melbourne amidst smoke storms resulting from one of the worst bushfire seasons in Australia’s history. ICSCE10 brought …
Why do some ferroelectric materials display bubble-shaped patterning, while others display complex, labyrinthine patterns? A FLEET study finds the answer to the changing patterns in ferroelectric films lies in non-equilibrium dynamics, with topological defects driving subsequent evolution. Ferroelectric materials can be considered an electrical analogy to ferromagnetic materials, with their permanent electric polarisation resembling the north and south poles of …
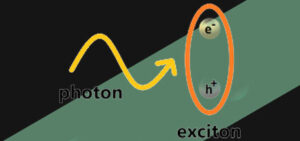
Enhanced interactions through strong light-matter coupling Why do two-dimensional exciton-polaritons interact? The intriguing quasiparticle the exciton-polariton is part light (photon), and part matter (exciton). Their excitonic (matter) part confers them the ability to interact with other particles —a property lacking to bare photons. In theory, when confined to only two dimensions, very slow (ie, very cold) excitons should cease any …
FLEET is committed to developing Australia’s next generation of science leaders, and to improving on the current imbalance of women in higher positions in STEM. Career support for women in FLEET works towards each of these two goals, providing an environment in which early-career women can thrive and progress, growing into capable and confident leaders. Four FLEET women were successful …
Spin-filtering could be the key to faster, more energy-efficient switching in future spintronic technology, allowing the detection of spin by electrical rather than magnetic means. A paper published last month by researchers at UNSW and international collaborators demonstrates spin detection using a spin filter to separate spin orientation according to their energies. Ultra-fast, ultra-low energy ‘spintronic’ devices are an exciting, …
Congratulations to ANU’s Matthias Wurdack on winning the AIP NSW Postgraduate Award this month for his presentation “Towards future low-energy transistor technologies with exciton-polariton superfluids in atomically thin semiconductors.” Matthias received the 2020 AIP Crystal Postgraduate figurine, and a $500 award from the Australian Institute of Physics. The NSW Branch of the Australian Institute of Physics in conjunction with the …
new thermoelectric materials could unlock body-heat powered personal devices, such as wrist-watches A new University of Wollongong study overcomes a major challenge of thermoelectric materials, which can convert heat into electricity and vice versa, improving conversion efficiency by more than 60%. Current and potential future applications range from low-maintenance, solid-state refrigeration to compact, zero-carbon power generation, which could include small, …
FLEET Chief Investigator Prof Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh has been named in the top 1% by citations in his field for the third year running. The Clarivate Analytics list identifies researchers ranking in the top 1% by citations for their field. The citation identifies influential researchers as determined by their peers around the globe – those who have consistently won recognition in …