Collaborate
Subscription confirmed
 WELCOME TO FLEET NEWS with regular updates from the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies.
WELCOME TO FLEET NEWS with regular updates from the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies.
Each edition of FLEET News brings a selection of research news from around the Centre, a wrap-up of FLEET stories in the media, outreach, and other news regarding FLEET researchers and research.
Catch up on past issues of FLEET News.
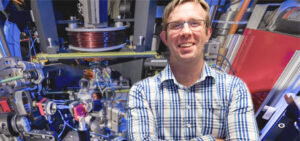
Michael Fuhrer
Director, FLEET
ARC Centre of Excellence in Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies
Following the news
 If you’re on Facebook, Twitter or Linkedin, you can follow our accounts to stay up to date with FLEET news and events. You can also follow news and events at FLEET.org.au.
If you’re on Facebook, Twitter or Linkedin, you can follow our accounts to stay up to date with FLEET news and events. You can also follow news and events at FLEET.org.au.
If a friend or colleague might be interested in our news, send them this link. Or let us know and we’ll invite them.
The challenge
 The big challenge that FLEET is addressing is the increasing energy load of computation, which is currently at least 5% of world electricity use, and doubling each decade.
The big challenge that FLEET is addressing is the increasing energy load of computation, which is currently at least 5% of world electricity use, and doubling each decade.
To date, the amount of energy being burned by computing has been kept in check by a phenomenon known as Moore’s Law, whereby the number of chips in a given area doubles every two years. But we are fast approaching a limit for Moore’s Law.
Current computing is based on semiconductor chips that each burn a tiny, tiny amount of power as they ‘switch’. FLEET will develop switches that will burn almost zero energy, operating at room temperature.
Our research
FLEET will use new concepts for electronic conduction without resistance to create a new generation of ultra-low energy electronics.
We will develop materials in which electricity can flow with minimal resistance and dissipation of heat, and devices in which that electric current can be switched on and off.
FLEET’s three Research Themes are:
- Topological materials (led by Alex Hamilton, UNSW)
- Exciton superfluids (Elena Ostrovskaya, ANU)
- Light-transformed materials (Kris Helmerson, Monash)
And this research is underpinned by two Technology themes:
- Fabrication of atomically thin materials (Xiaolin Wang, University of Wollongong)
- Nanodevice fabrication (Lan Wang, RMIT)
About FLEET

With over $40M investment from the ARC (Australian Research Council) and contributing organisations, FLEET will make a significant global impact in the electronics and energy sectors.
Headquartered at Monash University, and an ARC Centre of Excellence, FLEET has 19 chief investigators at seven Australian institutions, 17 partner investigators at 13 institutions worldwide, and will have over 100 higher-degree research students and postdoctoral fellows.
The highly interdisciplinary team includes some of Australia’s best researchers in atomic physics, condensed matter physics, materials science, electronics, nanofabrication and atomically thin materials.
By building strategic and strong partnerships with Australian and international industry, research institutions and government, FLEET will build capacity for advanced electronics research in Australia and train the workforce for the next generation of electronic materials researchers and future semiconductor industry.
Recent news
Exotic phase transitions unlock pathways to future, superfluid-based technologies. We can learn a lot by studying microscopic and macroscopic changes in a material as it crosses from one phase to another, for example from ice to water to steam. But while these phase transitions are well understood in the case of water, much less is known about the dynamics when …
An intrinsic magnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4 has been discovered with a large band gap, making it a promising material platform for fabricating ultra-low-energy electronics and observing exotic topological phenomena. Hosting both magnetism and topology, ultra-thin (only several nanometers in thickness) MnBi2Te4 was found to have a large band-gap in a Quantum Anomalous Hall (QAH) insulating state, where the material is …
2D kagome materials are a platform for tuneable electron-electron interactions ‘Star-like’ atomic-scale kagome geometry ‘switches on’ magnetism in a 2D organic material A 2D nanomaterial consisting of organic molecules linked to metal atoms in a specific atomic-scale geometry shows non-trivial electronic and magnetic properties due to strong interactions between its electrons. A new study, published today, shows the emergence of …
‘Growing’ electronic components directly onto a semiconductor block avoids messy, noisy oxidation scattering that slows and impedes electronic operation. A UNSW study out this month shows that the resulting high-mobility components are ideal candidates for high-frequency, ultra-small electronic devices, quantum dots, and for qubit applications in quantum computing. Smaller means faster, but also noisier Making computers faster requires ever-smaller transistors, …
Congratulations to FLEET Research Fellow Dr Iolanda Di Bernardo (Monash), who has received the highly prized Juan de la Cierva fellowship to fund research in Spain, starting in Spring 2022. The Juan de la Cierva fellowship is highly competitive, with a success rate between 10 and 15%, and is similar to the Australian DECRA fellowship. The grants encourage the recruitment …
Three FLEET Research Fellows are amongst those receiving DECRA Fellowships in ARC announcements this week. Congratulations to: Dr Matt Reeves (UQ) Calming the Superfluid Storm: Taming Turbulence in Superfluid Devices Dr Eli Estrecho (ANU) Mixing light and matter with complex gauge fields Dr Qingdong Ou (Monash) Engineering twisted 2D materials for mid-infrared detectors. Dr Matt Reeves (UQ) Calming the Superfluid …
Congratulations to FLEET AI Dr Zhi Li (UOW) who received an ARC Future Fellowship in this month’s announcement. The new ARC Fellowship will support Dr Li’s study of iron-based high-temperature topological superconductors, based at the Institute of Superconducting and Electronic Materials (ISEM) at the University of Wollongong. The topological non-trivial nature and zero resistance of topological superconductors make them very …
Talk to as many people as possible about your future career Stay open to new career directions Hi, I’m Paul Atkin. If we didn’t meet during my time as a FLEET scientist, we may have met more recently in my new life as a sales guy. If we haven’t met yet, I sincerely apologise and strongly suggest we meet for …
—first published APS Physics Electrons flow like a viscous fluid through a 2D channel with perfectly smooth sidewalls, offering a new platform to test solid-state and fluid dynamics theories. Electrons can, under certain conditions, flow like a fluid that’s thicker than honey. Now researchers have managed to observe this viscous fluid behavior in a way that allows unambiguous measurements and …
Monash review: joining topological insulators with magnetic materials for energy-efficient electronics A new Monash review throws the spotlight on recent research in heterostructures of topological insulators and magnetic materials. In such heterostructures, the interesting interplay of magnetism and topology can give rise to new phenomena such as quantum anomalous Hall insulators, axion insulators and skyrmions. All of these are promising …
A new ARC Research Hub highlighting the role of novel and 2D materials in emerging technologies in fields such as energy storage, purification and printed electronics features FLEET talent amongst its team. The ARC Research Hub for Advanced Manufacturing with 2D Materials (AM2D) will be led by Prof Mainak Majumder (Monash Department of Mechanical Engineering). Two FLEET Chief Investigators are amongst …
Tackling the next climate crisis with polariton superfluids, chocolate bars, ultra-fast laser pulses and chaotic gardening… FLEET’s Rishabh Mishra (Swinburne), Mitko Oldfield and Alex Nguyen (both at Monash University) have recently recorded explanations of their PhD research, submitted for the 2021 national Three Minute Thesis competition. Mitko Oldfield (School of Physics and Astronomy) explains his studies of polariton superfluids, with …
Fe-based superconductors reviewed The discovery of iron-based superconductors with a relatively high transition temperature Tc in 2008 opened a new chapter in the development of high-temperature superconductivity. The following decade saw a ‘research boom’ in superconductivity, with remarkable achievements in the theory, experiments and applications of iron-based superconductors, and in our understanding of the fundamental mechanism of superconductivity. A UOW …
Generating a topological anomalous Hall effect in a non-magnetic conductor anomalous planar Hall effect (APHE) the ‘smoking gun’ for the topological magnetic monopole in momentum space A FLEET theoretical study out this week has found a ‘smoking gun’ in the long search for the topological magnetic monopole referred to as the Berry curvature. This discovery is a breakthrough in the …
Congratulations to Jemima Goodhew (UQ) – the newest Women in FLEET Honours scholar – and Tommy Bartolo (RMIT), who has received a FLEET writeup scholarship. Jemima Goodhew has been working with FLEET CI Prof Matt Davis at UQ on computationally modelling a 2D superfluid Helmholtz resonator, driven by a chemical potential difference. She is particularly interested in the transition to and …