FLEET News
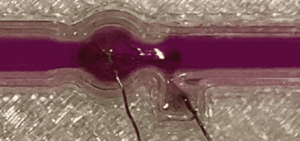
Liquid-metal machines could wipe out maintenance issues for continuous flow reactors. Metals that are liquid at room temperature, such as gallium and its alloys, are attractive materials due to their unique electrical, thermal and fluidic properties. In a study published today, a research team led by UNSW, Sydney has shown that liquid metals can offer their characteristics to the pharmaceutical and chemical …
Harnessing massive Dirac fermions in dual-magnetic-ion-doped Bi2Se3 topological insulator showing extremely strong quantum oscillations in the bulk. Double doping induces a gap for the topological surface state. A University of Wollongong-led team across three FLEET nodes has combined two traditional semiconductor doping methods to achieve new efficiencies in the topological insulator bismuth-selenide (Bi2Se3), Two doping elements were used: samarium (Sm) …
Welcome to FLEET’s long-time collaborator Dr Simon Granville, who this month joins the Centre as a Partner Investigator. Simon is a Principal Investigator at FLEET’s partner organisation the MacDiarmid Institute for Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology, where he leads the Institute’s Future Computing project to control electron transport and spin through superconductivity and topology. As a Senior Scientist at the Robinson …
Highly sensitive and with a rapid response time, the new X-ray detector is less than 10 nanometres thick and could potentially lead to real-time imaging of cellular biology. Exciton Science and FLEET researchers have used tin mono-sulfide (SnS) nanosheets to create the thinnest X-ray detector ever made, potentially enabling real-time imaging of cellular biology. X-ray detectors are tools that allow …
Spin-momentum locking induced anisotropic magnetoresistance in monolayer WTe2 Determining spin quantization axis, an essential element for fabricating spintronic devices, in 2D topological insulator WTe2 by measuring anisotropic magnetoresistance A RMIT-led, international collaboration published this week has observed large in-plane anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in a quantum spin Hall insulator and the spin quantization axis of the edge states can be well-defined. …
Diverse teams do better science. To maximise the effectiveness of our research team, and to improve diversity in Australian science, FLEET has added a new Diversity category to existing Women in FLEET fellowships, opening them up to a wider range of applicants from underrepresented groups in Australian STEM. Diversity in FLEET Fellowships are open to individuals from any group that …
–Are hover boards real? –What’s lightning? –Can we time travel? –Can I predict where a rainbow will form? –What is electricity, and who were the first electricians? Introducing FLEET’s new “Ask a physicist” page, where we’re encouraging schoolkids, parents and others to ask their hardest, most-baffling questions and we’ll answer them (or, we’ll find a FLEET member who can). We’d …
“FLEET’s strategic priorities include developing the next generation of science leaders, and fostering equity and diversity in STEM,” says FLEET Equity and Diversity Chair, Prof Jeff Davis. “Career and leadership support for women in FLEET works towards achieving both of these goals.” “FLEET will provide an environment for our early-career women to thrive and progress, growing into capable and confident …
A new Monash award honours the memory of FLEET’s Shaun Johnstone, who passed away in December 2019. The Shaun Johnstone Prize will be awarded for the best paper written by a PhD student in experimental physics or astronomy published in the past year. Shaun passed away from cancer not too long after receiving his PhD in experimental physics from Monash …
Developing transferable skills is vital for scientists at all career stages, but most particularly for PhDs and early-career researchers, to maximise their options inside and outside of academia. A team from across FLEET started the following list of resources, which are available for scientists to improve their skills… Thanks to Gol Akhgar and Semonti Bhattacharyya (Monash) Matthias Wurdack (ANU) and …
Innovative epitaxy technique creates a new phase of the popular multiferroic BiFeO3 Stress enhances the properties of a promising material for future technologies. UNSW researchers find a new exotic state of one of the most promising multiferroic materials, with exciting implications for future technologies using these enhanced properties. Combining a careful balance of thin-film strain, distortion, and thickness, the team …
New microcavity construction technique allows observation of robust, room-temperature exciton transport Polariton performance optimised by maximising photon-exciton energy exchange, minimizing the damage to monolayer A new ‘sandwich-style’ fabrication process placing a semiconductor only one atom thin between two mirrors has allowed Australian researchers to make a significant step towards ultra-low energy electronics based on the light-matter hybrid particles exciton-polaritons. The …
Driven states in WS2 monolayers unable to discriminate between ultrashort pulses of light and an infinite, continuous drive Ultrashort pulses of light can adiabatically drive transitions to new Floquet phases of matter Ultrashort pulses of light are proven indistinguishable from continuous illumination, in terms of controlling the electronic states of atomically-thin material tungsten disulfide (WS2). A new, Swinburne-led study proves …
Some alloys are in the liquid state at or near room temperature. These alloys are usually composed of gallium and indium (elements used in low energy lamps), tin and bismuth (materials used in constructions). The ratio and nature of elements in liquid alloys generate extraordinary phenomena on the surface of liquid metals which have been rarely explored to date and …