“The tunability of the SDE via multiple stimuli opens the way to many possible future device applications,” says lead author Dr Muhammad Nadeem (University of Wollongong)
A collaboration of FLEET researchers from the University of Wollongong and Monash University have reviewed the superconducting diode effect, one of the most fascinating phenomena recently discovered in quantum condensed-matter physics.
A superconducting diode enables dissipationless supercurrent to flow in only one direction, and provides new functionalities for superconducting circuits.
This non-dissipative circuit element is key to future ultra-low energy superconducting and semiconducting-superconducting hybrid quantum devices, with potential for quantum technologies in both classical and quantum computing.
Superconductors and diode effects
A superconductor is characterized by zero resistivity and perfect diamagnetic behavior, which leads to dissipationless transport and magnetic levitation.

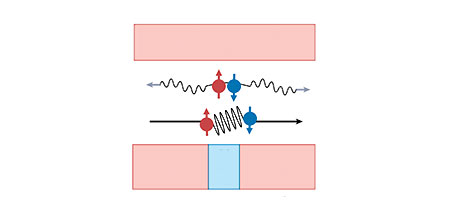
Superconducting diode effect in junction-free superconductors and Josephson junctions wherein supercurrent (paired electrons) flow in one direction while a normal current (unpaired electrons) flow in the other direction.
‘Conventional’ superconductors and the underlying phenomenon of low-temperature superconductivity are explained well by microscopic Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer (BCS) theory proposed in 1957.
The prediction of Fulde-Ferrell-Larkin-Ovchinnikov ferromagnetic superconducting phase in 1964-65 and the discovery of ‘high-temperature’ superconductivity in antiferromagnetic structures in 1986-87, has set the stage for the field of unconventional superconductivity wherein superconducting order can be stabilized in functional materials such as magnetic superconductors, ferroelectric superconductors, and helical or chiral topological superconductors.
Unlike conventional semiconductors and normal conductors, electrons in superconductors constitute pairs, known as Cooper pairs, and the flow of Cooper pairs is called a supercurrent.
Recently, researchers have observed nonreciprocal supercurrent transport leading to diode effects in various superconducting materials with different geometric structures and designs, including single crystals, thin films, heterostructures, nanowires, and Josephson junctions.
The study

SDEs offer significant improvements in their ability to be ‘tuned’, compared to conventional semiconductor diodes. Measured current-voltage plots show a vanishingly small diode effect in normal conductor (left) and a large tunable diode effect in superconductors (right)
The FLEET research team reviewed theoretical and experimental progress in the superconducting diode effect (SDE) and provided a prospective analysis of future aspects. This study sheds light on various materials hosting SDE, device structures, theoretical models, and symmetry requirements for different physical mechanisms leading to SDE.
“Unlike the conventional semiconducting diode, the efficiency of SDE is widely tunable via extrinsic stimuli such as temperature, magnetic field, gating, device design and intrinsic quantum mechanical functionalities such as Berry phase, band topology and spin-orbit interaction,” explains Dr. Muhammad Nadeem (University of Wollongong), who is a Research Fellow at FLEET.
The direction of supercurrent can be controlled either with a magnetic field or a gate electric field. “The gate-tunable diode functionalities in the field-effect superconducting structures could allow novel device applications for superconducting and semiconducting-superconducting hybrid technologies,” says co-author Prof Michael Fuhrer (Monash University), who is Director of FLEET.

The diode effects in a polar superconductor depends on a relative orientation of applied current (l), magnetic field (B), and polar axis (r), and thus, can be switched by reversing the direction of applied magnetic field.
SDE has been observed in a wide range of superconducting structures, made from conventional superconductors, ferroelectric superconductors, twisted few-layer graphene, van der Waals heterostructures, and helical or chiral topological superconductors. It reflects the enormous potential and wide usability of superconducting diodes, which markedly diversifies the landscape of quantum technologies, says Prof Xiaolin Wang (University of Wollongong), who is a Chief Investigator of FLEET.
The superconducting diode effect was published in Nature Reviews Physics in September 2023 (DOI: 10.1038/s42254-023-00632-w)
The Centre for Future Low-Energy Electronics Technologies (FLEET) is a collaboration of over a hundred researchers, seeking to develop ultra-low energy electronics to face the challenge of energy use in computation, which already consumes 8% of global electricity, and is doubling each decade.
More information
- Contact Muhammad Nadeem (University of Wollongong) mnadeem@uow.edu.au
- Contact Michael Fuhrer (Monash University) michael.fuhrer@monash.edu
- Contact Prof Xiaolin Wang (University of Wollongong) xiaolin@uow.edu.au
Dr. Muhammad Nadeem (University of Wollongong) is a Research Fellow in Prof Xiaolin Wang’s group at UOW node of FLEET, with a research focus on theoretical modelling and numerical simulations for low-energy quantum devices and technologies.
Prof Xiaolin Wang leads FLEET’s University of Wollongong node, as well as leading the Enabling Technology team developing the novel and atomically thin materials underpinning FLEET’s search for ultra-low energy electronics, managing synthesis and characterisation of novel 2D materials at the University of Wollongong. Prof Wang is also the Director of Institute of Superconducting and Electronic Materials, UOW.
Prof Michael Fuhrer (Monash University) is Director of FLEET and has pioneered studies of electronic properties of 2D materials, including synthesising and studying 2D topological insulators with large bandgaps in FLEET’s Research theme 1.